Java Feature :
The
inventors of Java wanted to design a language which could offer solutions to
some of the problems
encountered in modern programming. They wanted the language to be not only reliable, portable and distributed
but also simple, compact and interactive. Sun Microsystems officially describes Java with the following
attributes:
·
Compiled and
Interpreted
·
Platform-Independent
and Portable
· Object-Oriented
·
Robust and
Secure
· Distributed
·
Familiar,
Simple and Small
· Multithreaded and Interactive
·
High
Performance
· Dynamic and Extensible
Although the above appears to be a list of buzzwords, they
aptly describe the full potential of the language. These features have made Java the first
application language of the World Wide Web.
Java will also become the premier language for general purpose stand-alone
applications.
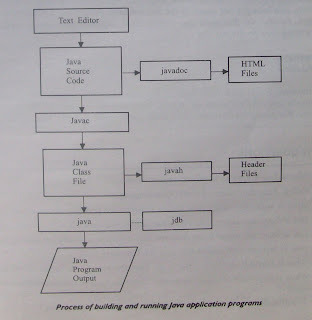
Compiled
and Interpreted
Usually
a computer language is either compiled or interpreted. Java combines both these
approaches thus making Java a two-stage system. First,
Java compiler translates source code into what is known as
bytecode instructions. Bytecodes are not machine instructions and therefore, in the second
stage, Java interpreter generates machine code that can be directly executed by the machine that is
running the Java program. We can thus say that Java is both a compiled and an interpreted language.
Platform-Independent and
Portable
The
most significant contribution of Java over other languages is its portability.
Jaya programs can be easily moved
from one computer system to another, anywhere and anytime. Changes and upgrades in operating systems, processors and
system resources will not force any changes in Java programs. This is the reason why Java has become a popular language
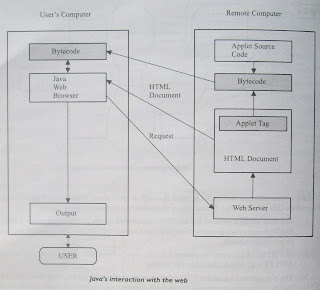
for programming on Internet which interconnects different kinds of
systems worldwide. We can download a Java applet from a remote computer onto
our local system via Internet and execute it locally. This makes the Internet
an extension of the user's basic system providing practically unlimited number
of accessible applets and applications.
Java
ensures portability in two ways. First. Java compiler generates bytecode
instructions that can be implemented on any machine. Secondly, the size of the
primitive data types are machine-independent.
Object-Oriented
Java is a true object-oriented language. Almost
everything in Java is an object. All program code and data reside within objects and classes. Java comes with an extensive
set of classes, arranged in packages, that we can use in our programs by inheritance.
The object model in Java is simple and easy to extend..
Robust and Secure
Java is a robust language. It provides many safeguards to ensure reliable code. It has strict compile time and run time checking for data types. It is designed as a garbage-collected language relieving the programmers virtually all memory management problems. Java also incorporates the concept of exception handling which captures series errors and eliminates any risk of crashing the system.
Security becomes an important issue for a language that is used for programming on Internet. Threat of viruses and abuse of resources is everywhere. Java systems not only verify all memory access but also ensure that no viruses are communicated with an applet. The absence of pointers in Java ensures that programs cannot gain access to memory locations without proper authorization.
Distributed
Java is designed as a distributed language for creating applications on networks. It has the ability to share both data and programs. Java applications can open and access remote objects on Internet as easily as they can do in a local system. This enables multiple programmers at multiple remote locations to collaborate and work together on a single project.
Simple, Small and Familiar
Java is a small and simple language. Many features of C and C++ that are either redundant or souree_s of unreliable code are not part of Java. For example, Java does not use pointers, preprocessor header tiles, goto statement and many others. It also eliminates operator overloading and multiple inheritance. For more detailed comparison of Java with C and C+ + .
Familiarity is another striking feature of Java. To make the language look familiar to the existing programmers, it was modelled on C and C+ + languages. Java uses many constructs of C and C++ and therefore, Java code "looks like a C+ +" code. In fact, Java is a simplified version of C+ +.
Multithreaded and Interactive
Multithreaded means handling multiple tasks simultaneously. Java supports multithreaded programs. This means that we need not wait for the application to finish one task before beginning another. For example. we can listen to an audio clip while scrolling a page and at the same time download an applet from a distant computer. This feature greatly improves the interactive performance of graphical applications.
The Java runtime comes with tools that support multiprocess synchronization and construct smoothly running interactive systems.
High Performance
Java performance is impressive for an interpreted language. mainly due to the use of intermediate byteeode. According to Sun, Java speed is comparable to the native C/C++. Java architecture is also designed to reduce overheads during runtime. Further, the incorporation of multithreading enhances the overall execution speed of Java programs.
Dynamic and Extensible
Java is a dynamic language. Java is capable of dynamically finking in new- class libraries. methods. and objects. Java can also determine the type of class through a query. making it possible to either dynamically link or abort the program. depending on the response.
Java programs support functions written in other languages such as C and C++. These functions are known as notice methods. This facility enables the programmers to use the efficient functions available in these languages. Native methods are linked dynamically at runtime.